Portal:Computer programming
q
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application ___domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of May 2023[update], the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally.
Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–1852), who has been credited as the first computer programmer. (Full article...) -
Image 2Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily as a declarative programming language: the program is a set of facts and rules, which define relations. A computation is initiated by running a query over the program.
Prolog was one of the first logic programming languages and remains the most popular such language today, with several free and commercial implementations available. The language has been used for theorem proving, expert systems, term rewriting, type systems, and automated planning, as well as its original intended field of use, natural language processing. (Full article...) -
Image 3
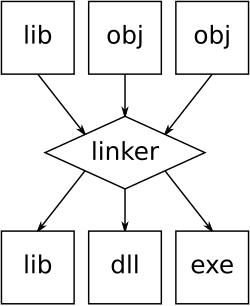
An illustration of the linking process. Object files and static libraries are assembled into a new library or executable
A linker or link editor is a computer program that combines intermediate software build files such as object and library files into a single executable file such as a program or library. A linker is often part of a toolchain that includes a compiler and/or assembler that generates intermediate files that the linker processes. The linker may be integrated with other toolchain tools such that the user does not interact with the linker directly.
A simpler version that writes its output directly to memory is called the loader, though loading is typically considered a separate process. (Full article...) -
Image 4Programming languages are used for controlling the behavior of a machine (often a computer). Like natural languages, programming languages follow rules for syntax and semantics.
There are thousands of programming languages and new ones are created every year. Few languages ever become sufficiently popular that they are used by more than a few people, but professional programmers may use dozens of languages in a career.
Most programming languages are not standardized by an international (or national) standard, even widely used ones, such as Perl or Standard ML (despite the name). Notable standardized programming languages include ALGOL, C, C++, JavaScript (under the name ECMAScript), Smalltalk, Prolog, Common Lisp, Scheme (IEEE standard), ISLISP, Ada, Fortran, COBOL, SQL, and XQuery. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Tcl (pronounced "tickle" or "TCL"; originally Tool Command Language) is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. It was designed with the goal of being very simple but powerful. Tcl casts everything into the mold of a command, even programming constructs like variable assignment and procedure definition. Tcl supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative, functional, and procedural styles.
It is commonly used embedded into C applications, for rapid prototyping, scripted applications, GUIs, and testing. Tcl interpreters are available for many operating systems, allowing Tcl code to run on a wide variety of systems. Because Tcl is a very compact language, it is used on embedded systems platforms, both in its full form and in several other small-footprint versions.
The popular combination of Tcl with the Tk extension is referred to as Tcl/Tk (pronounced "tickle teak"[citation needed] or "tickle TK") and enables building a graphical user interface (GUI) natively in Tcl. Tcl/Tk is included in the standard Python installation in the form of Tkinter. (Full article...) -
Image 6

PHP is a general-purpose scripting language geared towards web development. It was originally created by Danish-Canadian programmer Rasmus Lerdorf in 1993 and released in 1995. The PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP Group. PHP was originally an abbreviation of Personal Home Page, but it now stands for the recursive backronym PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
PHP code is usually processed on a web server by a PHP interpreter implemented as a module, a daemon or a Common Gateway Interface (CGI) executable. On a web server, the result of the interpreted and executed PHP code—which may be any type of data, such as generated HTML or binary image data—would form the whole or part of an HTTP response. Various web template systems, web content management systems, and web frameworks exist that can be employed to orchestrate or facilitate the generation of that response. Additionally, PHP can be used for many programming tasks outside the web context, such as standalone graphical applications and drone control. PHP code can also be directly executed from the command line.
The standard PHP interpreter, powered by the Zend Engine, is free software released under the PHP License. PHP has been widely ported and can be deployed on most web servers on a variety of operating systems and platforms. (Full article...) -
Image 7

R is a programming language for statistical computing and data visualization. It has been widely adopted in the fields of data mining, bioinformatics, data analysis, and data science.
The core R language is extended by a large number of software packages, which contain reusable code, documentation, and sample data. Some of the most popular R packages are in the tidyverse collection, which enhances functionality for visualizing, transforming, and modelling data, as well as improves the ease of programming (according to the authors and users).
R is free and open-source software distributed under the GNU General Public License. The language is implemented primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself. Precompiled executables are available for the major operating systems (including Linux, MacOS, and Microsoft Windows). (Full article...) -
Image 8

Scala (/ˈskɑːlɑː/ SKAH-lah) is a strongly statically typed high-level general-purpose programming language that supports both object-oriented programming and functional programming. Designed to be concise, many of Scala's design decisions are intended to address criticisms of Java.
Scala source code can be compiled to Java bytecode and run on a Java virtual machine (JVM). Scala can also be transpiled to JavaScript to run in a browser, or compiled directly to a native executable. When running on the JVM, Scala provides language interoperability with Java so that libraries written in either language may be referenced directly in Scala or Java code. Like Java, Scala is object-oriented, and uses a syntax termed curly-brace which is similar to the language C. Since Scala 3, there is also an option to use the off-side rule (indenting) to structure blocks, and its use is advised. Martin Odersky has said that this turned out to be the most productive change introduced in Scala 3.
Unlike Java, Scala has many features of functional programming languages (like Scheme, Standard ML, and Haskell), including currying, immutability, lazy evaluation, and pattern matching. It also has an advanced type system supporting algebraic data types, covariance and contravariance, higher-order types (but not higher-rank types), anonymous types, operator overloading, optional parameters, named parameters, raw strings, and an experimental exception-only version of algebraic effects that can be seen as a more powerful version of Java's checked exceptions. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Yoshua Bengio OC OQ FRS FRSC (born March 5, 1964) is a Canadian computer scientist, and a pioneer of artificial neural networks and deep learning. He is a professor at the Université de Montréal and scientific director of the AI institute MILA.
Bengio received the 2018 ACM A.M. Turing Award, often referred to as the "Nobel Prize of Computing", together with Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun, for their foundational work on deep learning. Bengio, Hinton, and LeCun are sometimes referred to as the "Godfathers of AI". Bengio is the most-cited computer scientist globally (by both total citations and by h-index), and the most-cited living scientist across all fields (by total citations). In 2024, TIME Magazine included Bengio in its yearly list of the world's 100 most influential people. (Full article...) -
Image 10Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, contextual information norms, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection. (Full article...)
-
Image 11
Swift is a high-level general-purpose, multi-paradigm, compiled programming language created by Chris Lattner in 2010 for Apple Inc. and maintained by the open-source community. Swift compiles to machine code and uses an LLVM-based compiler. Swift was first released in June 2014 and the Swift toolchain has shipped in Xcode since Xcode version 6, released in September 2014.
Apple intended Swift to support many core concepts associated with Objective-C, notably dynamic dispatch, widespread late binding, extensible programming, and similar features, but in a "safer" way, making it easier to catch software bugs; Swift has features addressing some common programming errors like null pointer dereferencing and provides syntactic sugar to help avoid the pyramid of doom. Swift supports the concept of protocol extensibility, an extensibility system that can be applied to types, structs and classes, which Apple promotes as a real change in programming paradigms they term "protocol-oriented programming" (similar to traits and type classes).
Swift was introduced at Apple's 2014 Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC). It underwent an upgrade to version 1.2 during 2014 and a major upgrade to Swift 2 at WWDC 2015. It was initially a proprietary language, but version 2.2 was made open-source software under the Apache License 2.0 on December 3, 2015, for Apple's platforms and Linux. (Full article...) -
Image 12

tcsh and sh shell windows on a Mac OS X Leopard desktop
A Unix shell is a shell that provides a command-line user interface for a Unix-like operating system. A Unix shell provides a command language that can be used either interactively or for writing a shell script. A user typically interacts with a Unix shell via a terminal emulator; however, direct access via serial hardware connections or Secure Shell are common for server systems. Although use of a Unix shell is popular with some users, others prefer to use a windowing system such as desktop Linux distribution or macOS instead of a command-line interface.
A user may have access to multiple Unix shells with one configured to run by default when the user logs in interactively. The default selection is typically stored in a user's profile; for example, in the local passwd file or in a distributed configuration system such as NIS or LDAP. A user may use other shells nested inside the default shell.
A Unix shell may provide many features including: variable definition and substitution, command substitution, filename wildcarding, stream piping, control flow structures (condition-testing and iteration), working directory context, and here document. (Full article...) -
Image 13COBOL (/ˈkoʊbɒl, -bɔːl/; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural, and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily used in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments. COBOL is still widely used in applications deployed on mainframe computers, such as large-scale batch and transaction processing jobs. Many large financial institutions were developing new systems in the language as late as 2006, but most programming in COBOL today is purely to maintain existing applications. Programs are being moved to new platforms, rewritten in modern languages, or replaced with other software.
COBOL was designed in 1959 by CODASYL and was partly based on the programming language FLOW-MATIC, designed by Grace Hopper. It was created as part of a U.S. Department of Defense effort to create a portable programming language for data processing. It was originally seen as a stopgap, but the Defense Department promptly pressured computer manufacturers to provide it, resulting in its widespread adoption. It was standardized in 1968 and has been revised five times. Expansions include support for structured and object-oriented programming. The current standard is ISO/IEC 1989:2023.
COBOL statements have prose syntax such asMOVE x TO y, which was designed to be self-documenting and highly readable. However, it is verbose and uses over 300 reserved words compared to the succinct and mathematically inspired syntax of other languages. (Full article...) -
Image 14Logotype used on the cover of the first edition of The C Programming Language
C is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains widely used and influential. By design, C gives the programmer relatively direct access to the features of the typical CPU architecture, customized for the target instruction set. It has been and continues to be used to implement operating systems (especially kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is used on computers that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems.
A successor to the programming language B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming languages, with C compilers available for practically all modern computer architectures and operating systems. The book The C Programming Language, co-authored by the original language designer, served for many years as the de facto standard for the language. C has been standardized since 1989 by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and, subsequently, jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
C is an imperative procedural language, supporting structured programming, lexical variable scope, and recursion, with a static type system. It was designed to be compiled to provide low-level access to memory and language constructs that map efficiently to machine instructions, all with minimal runtime support. Despite its low-level capabilities, the language was designed to encourage cross-platform programming. A standards-compliant C program written with portability in mind can be compiled for a wide variety of computer platforms and operating systems with few changes to its source code. (Full article...) -
Image 15

Rust is a general-purpose programming language emphasizing performance, type safety, and concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all references point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references at compile time.
Rust supports multiple programming paradigms. It was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, enums, traits, and methods.
Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at Mozilla Research in 2006. Mozilla officially sponsored the project in 2009. The first stable release of Rust, Rust 1.0, was published in May 2015. Following a large layoff of Mozilla employees in August 2020, multiple other companies joined Mozilla in sponsoring Rust through the creation of the Rust Foundation in February 2021. In December 2022, Rust became the first language other than C and assembly to be supported in the development of the Linux kernel. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
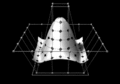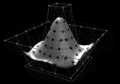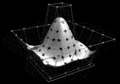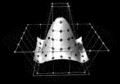
Image 1Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 2Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 3Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 4This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 6A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 7Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 10A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 11Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 12A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 13Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 14Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 16GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
Image 17An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
-
Image 18Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that the study of selection algorithms has been traced to an 1883 work of Lewis Carroll on how to award second place in single-elimination tournaments?
- ... that a "hacker" with blog posts written by ChatGPT was at the center of an online scavenger hunt promoting Avenged Sevenfold's album Life Is but a Dream...?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that the programming language Acorn System BASIC was so non-standard that one commenter suggested that using it on the BBC Micro would be a disaster?
- ... that Cornell University's student-oriented programming language dialect was made available to other universities but required a "research grant" payment in exchange?
- ... that the Gale–Shapley algorithm was used to assign medical students to residencies long before its publication by Gale and Shapley?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
Lua error: Unmatched close-bracket at pattern character 44.
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

![Image 1 Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of May 2023[update], the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally. Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–1852), who has been credited as the first computer programmer. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)