Portal:Computer programming
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application ___domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1
Yoshua Bengio OC OQ FRS FRSC (born March 5, 1964) is a Canadian computer scientist, and a pioneer of artificial neural networks and deep learning. He is a professor at the Université de Montréal and scientific director of the AI institute MILA.
Bengio received the 2018 ACM A.M. Turing Award, often referred to as the "Nobel Prize of Computing", together with Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun, for their foundational work on deep learning. Bengio, Hinton, and LeCun are sometimes referred to as the "Godfathers of AI". Bengio is the most-cited computer scientist globally (by both total citations and by h-index), and the most-cited living scientist across all fields (by total citations). In 2024, TIME Magazine included Bengio in its yearly list of the world's 100 most influential people. (Full article...) -
Image 2

D, also known as dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is now a very different language. As it has developed, it has drawn inspiration from other high-level programming languages. Notably, it has been influenced by Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.
The D language reference describes it as follows: (Full article...) -
Image 3
JavaScript (JS) is a programming language and core technology of the web platform, alongside HTML and CSS. Ninety-nine percent of websites on the World Wide Web use JavaScript on the client side for webpage behavior.
Web browsers have a dedicated JavaScript engine that executes the client code. These engines are also utilized in some servers and a variety of apps. The most popular runtime system for non-browser usage is Node.js.
JavaScript is a high-level, often just-in-time–compiled language that conforms to the ECMAScript standard. It has dynamic typing, prototype-based object-orientation, and first-class functions. It is multi-paradigm, supporting event-driven, functional, and imperative programming styles. It has application programming interfaces (APIs) for working with text, dates, regular expressions, standard data structures, and the Document Object Model (DOM). (Full article...) -
Image 4

W3sDesign Interpreter Design Pattern UML
In computing, an interpreter is software that directly executes encoded logic. Use of an interpreter contrasts the direct execution of CPU-native executable code that typically involves compiling source code to machine code. Input to an interpreter conforms to a programming language which may be a traditional, well-defined language (such as JavaScript), but could alternatively be a custom language or even a relatively trivial data encoding such as a control table.
Historically, programs were either compiled to machine code for native execution or interpreted. Over time, many hybrid approaches were developed. Early versions of Lisp and BASIC runtime environments parsed source code and performed its implied behavior directly. The runtime environments for Perl, Raku, Python, MATLAB, and Ruby translate source code into an intermediate format before executing to enhance runtime performance. The .NET and Java eco-systems use bytecode for an intermediate format, but in some cases the runtime environment translates the bytecode to machine code (via Just-in-time compilation) instead of interpreting the bytecode directly.
Although each programming language is usually associated with a particular runtime environment, a language can be used in different environments. For example interpreters have been constructed for languages traditionally associated with compilation, such as ALGOL, Fortran, COBOL, C and C++. Thus, the terms interpreted language and compiled language, although commonly used, have little meaning. (Full article...) -
Image 5
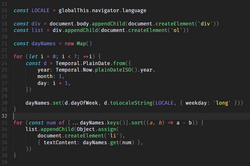
Source code for a computer program written in the JavaScript language. It demonstrates the appendChild method. The method adds a new child node to an existing parent node. It is commonly used to dynamically modify the structure of an HTML document.
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. It is one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter written for the language.
If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. (Full article...) -
Image 6In the C++ programming language,
decltypeis a keyword used to query the type of an expression. Introduced in C++11, its primary intended use is in generic programming, where it is often difficult, or even impossible, to express types that depend on template parameters.
As generic programming techniques became increasingly popular throughout the 1990s, the need for a type-deduction mechanism was recognized. Many compiler vendors implemented their own versions of the operator, typically calledtypeof, and some portable implementations with limited functionality, based on existing language features were developed. In 2002, Bjarne Stroustrup proposed that a standardized version of the operator be added to the C++ language, and suggested the name "decltype", to reflect that the operator would yield the "declared type" of an expression.decltype's semantics were designed to cater to both generic library writers and novice programmers. In general, the deduced type matches the type of the object or function exactly as declared in the source code. Like thesizeofoperator,decltype's operand is not evaluated. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Ada is a structured, statically typed, imperative, and object-oriented high-level programming language, inspired by Pascal and other languages. It has built-in language support for design by contract (DbC), extremely strong typing, explicit concurrency, tasks, synchronous message passing, protected objects, and non-determinism. Ada improves code safety and maintainability by using the compiler to find errors in favor of runtime errors. Ada is an international technical standard, jointly defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). As of May 2023[update], the standard, ISO/IEC 8652:2023, is called Ada 2022 informally.
Ada was originally designed by a team led by French computer scientist Jean Ichbiah of Honeywell under contract to the United States Department of Defense (DoD) from 1977 to 1983 to supersede over 450 programming languages then used by the DoD. Ada was named after Ada Lovelace (1815–1852), who has been credited as the first computer programmer. (Full article...) -
Image 8Lisp (historically LISP, an abbreviation of "list processing") is a family of programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized prefix notation.
Originally specified in the late 1950s, it is the second-oldest high-level programming language still in common use, after Fortran. Lisp has changed since its early days, and many dialects have existed over its history. Today, the best-known general-purpose Lisp dialects are Common Lisp, Scheme, Racket, and Clojure.
Lisp was originally created as a practical mathematical notation for computer programs, influenced by (though not originally derived from) the notation of Alonzo Church's lambda calculus. It quickly became a favored programming language for artificial intelligence (AI) research. As one of the earliest programming languages, Lisp pioneered many ideas in computer science, including tree data structures, automatic storage management, dynamic typing, conditionals, higher-order functions, recursion, the self-hosting compiler, and the read–eval–print loop.
The name LISP derives from "LISt Processor". Linked lists are one of Lisp's major data structures, and Lisp source code is made of lists. Thus, Lisp programs can manipulate source code as a data structure, giving rise to the macro systems that allow programmers to create new syntax or new ___domain-specific languages embedded in Lisp. (Full article...) -
Image 9Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily as a declarative programming language: the program is a set of facts and rules, which define relations. A computation is initiated by running a query over the program.
Prolog was one of the first logic programming languages and remains the most popular such language today, with several free and commercial implementations available. The language has been used for theorem proving, expert systems, term rewriting, type systems, and automated planning, as well as its original intended field of use, natural language processing. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Rust is a general-purpose programming language emphasizing performance, type safety, and concurrency. It enforces memory safety, meaning that all references point to valid memory. It does so without a conventional garbage collector; instead, memory safety errors and data races are prevented by the "borrow checker", which tracks the object lifetime of references at compile time.
Rust supports multiple programming paradigms. It was influenced by ideas from functional programming, including immutability, higher-order functions, algebraic data types, and pattern matching. It also supports object-oriented programming via structs, enums, traits, and methods.
Software developer Graydon Hoare created Rust as a personal project while working at Mozilla Research in 2006. Mozilla officially sponsored the project in 2009. The first stable release of Rust, Rust 1.0, was published in May 2015. Following a large layoff of Mozilla employees in August 2020, multiple other companies joined Mozilla in sponsoring Rust through the creation of the Rust Foundation in February 2021. In December 2022, Rust became the first language other than C and assembly to be supported in the development of the Linux kernel. (Full article...) -
Image 11

A computer lab contains a wide range of information technology elements,
including hardware, software and storage systems.
Information technology (IT) is the study or use of computers, telecommunication systems and other devices to create, process, store, retrieve and transmit information. While the term is commonly used to refer to computers and computer networks, it also encompasses other information distribution technologies such as television and telephones. Information technology is an application of computer science and computer engineering.
An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a computer system — including all hardware, software, and peripheral equipment — operated by a limited group of IT users, and an IT project usually refers to the commissioning and implementation of an IT system. IT systems play a vital role in facilitating efficient data management, enhancing communication networks, and supporting organizational processes across various industries. Successful IT projects require meticulous planning and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal functionality and alignment with organizational objectives.
Although humans have been storing, retrieving, manipulating, analysing and communicating information since the earliest writing systems were developed, the term information technology in its modern sense first appeared in a 1958 article published in the Harvard Business Review; authors Harold J. Leavitt and Thomas L. Whisler commented that "the new technology does not yet have a single established name. We shall call it information technology (IT)." Their definition consists of three categories: techniques for processing, the application of statistical and mathematical methods to decision-making, and the simulation of higher-order thinking through computer programs. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Go is a high-level general purpose programming language that is statically typed and compiled. It is known for the simplicity of its syntax and the efficiency of development that it enables by the inclusion of a large standard library supplying many needs for common projects. It was designed at Google in 2007 by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson, and publicly announced in November of 2009. It is syntactically similar to C, but also has garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency. It is often referred to as Golang to avoid ambiguity and because of its former ___domain name,golang.org, but its proper name is Go.
There are two major implementations:- The original, self-hosting compiler toolchain, initially developed inside Google;
- A frontend written in C++, called gofrontend, originally a GCC frontend, providing gccgo, a GCC-based Go compiler; later extended to also support LLVM, providing an LLVM-based Go compiler called gollvm.
-
Image 13Ronald Paul "Ron" Fedkiw (born February 27, 1968) is a full professor in the Stanford University department of computer science and a leading researcher in the field of computer graphics, focusing on topics relating to physically based simulation of natural phenomena and machine learning. His techniques have been employed in many motion pictures. He has earned recognition at the 80th Academy Awards and the 87th Academy Awards as well as from the National Academy of Sciences.
His first Academy Award was awarded for developing techniques that enabled many technically sophisticated adaptations including the visual effects in 21st century movies in the Star Wars, Harry Potter, Terminator, and Pirates of the Caribbean franchises. Fedkiw has designed a platform that has been used to create many of the movie world's most advanced special effects since it was first used on the T-X character in Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines. His second Academy Award was awarded for computer graphics techniques for special effects for large scale destruction. Although he has won an Oscar for his work, he does not design the visual effects that use his technique. Instead, he has developed a system that other award-winning technicians and engineers have used to create visual effects for some of the world's most expensive and highest-grossing movies. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Erlang (/ˈɜːrlæŋ/ UR-lang) is a general-purpose, concurrent, functional high-level programming language, and a garbage-collected runtime system. The term Erlang is used interchangeably with Erlang/OTP, or Open Telecom Platform (OTP), which consists of the Erlang runtime system, several ready-to-use components (OTP) mainly written in Erlang, and a set of design principles for Erlang programs.
The Erlang runtime system is designed for systems with these traits:- Distributed
- Fault-tolerant
- Soft real-time
- Highly available, non-stop applications
- Hot swapping, where code can be changed without stopping a system.
-
Image 15

Scala (/ˈskɑːlɑː/ SKAH-lah) is a strongly statically typed high-level general-purpose programming language that supports both object-oriented programming and functional programming. Designed to be concise, many of Scala's design decisions are intended to address criticisms of Java.
Scala source code can be compiled to Java bytecode and run on a Java virtual machine (JVM). Scala can also be transpiled to JavaScript to run in a browser, or compiled directly to a native executable. When running on the JVM, Scala provides language interoperability with Java so that libraries written in either language may be referenced directly in Scala or Java code. Like Java, Scala is object-oriented, and uses a syntax termed curly-brace which is similar to the language C. Since Scala 3, there is also an option to use the off-side rule (indenting) to structure blocks, and its use is advised. Martin Odersky has said that this turned out to be the most productive change introduced in Scala 3.
Unlike Java, Scala has many features of functional programming languages (like Scheme, Standard ML, and Haskell), including currying, immutability, lazy evaluation, and pattern matching. It also has an advanced type system supporting algebraic data types, covariance and contravariance, higher-order types (but not higher-rank types), anonymous types, operator overloading, optional parameters, named parameters, raw strings, and an experimental exception-only version of algebraic effects that can be seen as a more powerful version of Java's checked exceptions. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 1A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 2Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 3Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 5Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 6Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
-
Image 7A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 10Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 11An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
-
Image 12Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 13GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
Image 14Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 15A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 17Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 18This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that a "hacker" with blog posts written by ChatGPT was at the center of an online scavenger hunt promoting Avenged Sevenfold's album Life Is but a Dream...?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that both Thackeray and Longfellow bought paintings by Fanny Steers?
- ... that the 2024 psychological horror game Mouthwashing utilises non-diegetic scene transitions that mimic glitches and crashes?
- ... that Cornell University's student-oriented programming language dialect was made available to other universities but required a "research grant" payment in exchange?
- ... that a pink skin for Mercy in the video game Overwatch helped raise more than $12 million for breast cancer research?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
No recent news
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus