Portal:Computer programming
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application ___domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1Information privacy is the relationship between the collection and dissemination of data, technology, the public expectation of privacy, contextual information norms, and the legal and political issues surrounding them. It is also known as data privacy or data protection. (Full article...)
-
Image 2Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily as a declarative programming language: the program is a set of facts and rules, which define relations. A computation is initiated by running a query over the program.
Prolog was one of the first logic programming languages and remains the most popular such language today, with several free and commercial implementations available. The language has been used for theorem proving, expert systems, term rewriting, type systems, and automated planning, as well as its original intended field of use, natural language processing. (Full article...) -
Image 3The Antikythera mechanism (/ˌæntɪkɪˈθɪərə/ AN-tik-ih-THEER-ə, US also /ˌæntaɪkɪˈ-/ AN-ty-kih-) is an ancient Greek hand-powered orrery (model of the Solar System). It is the oldest known example of an analogue computer. It could be used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games similar to an olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games.
The artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. In 1902, during a visit to the National Archaeological Museum in Athens, it was noticed by Greek politician Spyridon Stais as containing a gear, prompting the first study of the fragment by his cousin, Valerios Stais, the museum director. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size 34 cm × 18 cm × 9 cm (13.4 in × 7.1 in × 3.5 in), was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is about 13 cm (5 in) in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. All these fragments of the mechanism are kept at the National Archaeological Museum, along with reconstructions and replicas, to demonstrate how it may have looked and worked.
In 2005, a team from Cardiff University led by Mike Edmunds used computer X-ray tomography and high resolution scanning to image inside fragments of the crust-encased mechanism and read the faintest inscriptions that once covered the outer casing. These scans suggest that the mechanism had 37 meshing bronze gears enabling it to follow the movements of the Moon and the Sun through the zodiac, to predict eclipses and to model the irregular orbit of the Moon, where the Moon's velocity is higher in its perigee than in its apogee. This motion was studied in the 2nd century BC by astronomer Hipparchus of Rhodes, and he may have been consulted in the machine's construction. There is speculation that a portion of the mechanism is missing and it calculated the positions of the five classical planets. The inscriptions were further deciphered in 2016, revealing numbers connected with the synodic cycles of Venus and Saturn. (Full article...) -
Image 4
William Henry Gates III CFR (born October 28, 1955) is an American businessman and philanthropist. A pioneer of the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, he co-founded the software company Microsoft in 1975 with his childhood friend Paul Allen. Following the company's 1986 initial public offering (IPO), Gates became a billionaire in 1987—then the youngest ever, at age 31. Forbes magazine ranked him as the world's wealthiest person for 18 out of 24 years between 1995 and 2017, including 13 years consecutively from 1995 to 2007. He became the first centibillionaire in 1999, when his net worth briefly surpassed $100 billion. According to Forbes, as of May 2025, his net worth stood at US$115.1 billion, making him the thirteenth-richest individual in the world.
Born and raised in Seattle, Washington, Gates was privately educated at Lakeside School, where he befriended Allen and developed his computing interests. In 1973, he enrolled at Harvard University, where he took classes including Math 55 and graduate level computer science courses, but he dropped out in 1975 to co-found and lead Microsoft. He served as its CEO for the next 25 years and also became president and chairman of the board when the company incorporated in 1981. Succeeded as CEO by Steve Ballmer in 2000, he transitioned to chief software architect, a position he held until 2008. He stepped down as chairman of the board in 2014 and became technology adviser to CEO Satya Nadella and other Microsoft leaders, a position he still holds. He resigned from the board in 2020.
Over time, Gates reduced his role at Microsoft to focus on his philanthropic work with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the world's largest private charitable organization, which he and his then-wife Melinda French Gates co-chaired from 2000 until 2024. Focusing on areas including health, education, and poverty alleviation, Gates became known for his efforts to eradicate transmissible diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, and polio. After French Gates resigned as co-chair following the couple's divorce, the foundation was renamed the Gates Foundation, with Gates as its sole chair. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Charles Babbage KH FRS (/ˈbæbɪdʒ/; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered by some to merit the title of "father of the computer". He is credited with inventing the first mechanical computer, the difference engine, that eventually led to more complex electronic designs, though all the essential ideas of modern computers are to be found in his analytical engine, programmed using a principle openly borrowed from the Jacquard loom. As part of his computer work, he also designed the first computer printers. He had a broad range of interests in addition to his work on computers, covered in his 1832 book Economy of Manufactures and Machinery. He was an important figure in the social scene in London, and is credited with importing the "scientific soirée" from France with his well-attended Saturday evening soirées. His varied work in other fields has led him to be described as "pre-eminent" among the many polymaths of his century.
Babbage, who died before the complete successful engineering of many of his designs, including his Difference Engine and Analytical Engine, remained a prominent figure in the ideating of computing. Parts of his incomplete mechanisms are on display in the Science Museum in London. In 1991, a functioning difference engine was constructed from the original plans. Built to tolerances achievable in the 19th century, the success of the finished engine indicated that Babbage's machine would have worked. (Full article...) -
Image 6Atari BASIC (1979) for Atari 8-bit computers
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1964. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn.
In addition to the programming language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their history to one of these versions of BASIC.
The emergence of microcomputers in the mid-1970s led to the development of multiple BASIC dialects, including Microsoft BASIC in 1975. Due to the tiny main memory available on these machines, often 4 KB, a variety of Tiny BASIC dialects were also created. BASIC was available for almost any system of the era and became the de facto programming language for home computer systems that emerged in the late 1970s. These PCs almost always had a BASIC interpreter installed by default, often in the machine's firmware or sometimes on a ROM cartridge. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Julia is a dynamic general-purpose programming language. As a high-level language, distinctive aspects of Julia's design include a type system with parametric polymorphism, the use of multiple dispatch as a core programming paradigm, just-in-time (JIT) compilation and a parallel garbage collection implementation. Notably Julia does not support classes with encapsulated methods but instead relies on the types of all of a function's arguments to determine which method will be called.
By default, Julia is run similarly to scripting languages, using its runtime, and allows for interactions, but Julia programs/source code can also optionally be sent to users in one ready-to-install/run file, which can be made quickly, not needing anything preinstalled.
Julia programs can reuse libraries from other languages (or itself be reused from other); Julia has a special no-boilerplate keyword allowing calling e.g. C, Fortran or Rust libraries, and e.g. PythonCall.jl uses it indirectly for you, and Julia (libraries) can also be called from other languages, e.g. Python and R, and several Julia packages have been made easily available from those languages, in the form of Python and R libraries for corresponding Julia packages. Calling in either direction has been implemented for many languages, not just those and C++. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Erlang (/ˈɜːrlæŋ/ UR-lang) is a general-purpose, concurrent, functional high-level programming language, and a garbage-collected runtime system. The term Erlang is used interchangeably with Erlang/OTP, or Open Telecom Platform (OTP), which consists of the Erlang runtime system, several ready-to-use components (OTP) mainly written in Erlang, and a set of design principles for Erlang programs.
The Erlang runtime system is designed for systems with these traits:- Distributed
- Fault-tolerant
- Soft real-time
- Highly available, non-stop applications
- Hot swapping, where code can be changed without stopping a system.
-
Image 9

Go is a high-level general purpose programming language that is statically typed and compiled. It is known for the simplicity of its syntax and the efficiency of development that it enables by the inclusion of a large standard library supplying many needs for common projects. It was designed at Google in 2007 by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson, and publicly announced in November of 2009. It is syntactically similar to C, but also has garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency. It is often referred to as Golang to avoid ambiguity and because of its former ___domain name,golang.org, but its proper name is Go.
There are two major implementations:- The original, self-hosting compiler toolchain, initially developed inside Google;
- A frontend written in C++, called gofrontend, originally a GCC frontend, providing gccgo, a GCC-based Go compiler; later extended to also support LLVM, providing an LLVM-based Go compiler called gollvm.
-
Image 10Object Pascal is an extension to the programming language Pascal that provides object-oriented programming (OOP) features such as classes and methods.
The language was originally developed by Apple Computer as Clascal for the Lisa Workshop development system. As Lisa gave way to Macintosh, Apple collaborated with Niklaus Wirth, the author of Pascal, to develop an officially standardized version of Clascal. This was renamed Object Pascal. Through the mid-1980s, Object Pascal was the main programming language for early versions of the MacApp application framework. The language lost its place as the main development language on the Mac in 1991 with the release of the C++-based MacApp 3.0. Official support ended in 1996.
Symantec also developed a compiler for Object Pascal for their Think Pascal product, which could compile programs much faster than Apple's own Macintosh Programmer's Workshop (MPW). Symantec then developed the Think Class Library (TCL), based on MacApp concepts, which could be called from both Object Pascal and THINK C. The Think suite largely displaced MPW as the main development platform on the Mac in the late 1980s. (Full article...) -
Image 11Forth is a stack-oriented programming language and interactive integrated development environment designed by Charles H. "Chuck" Moore and first used by other programmers in 1970.
Although not an acronym, the language's name in its early years was often spelled in all capital letters as FORTH.
The FORTH-79 and FORTH-83 implementations, which were not written by Moore, became de facto standards, and an official technical standard of the language was published in 1994 as ANS Forth.
A wide range of Forth derivatives existed before and after ANS Forth.
The free and open-source software Gforth implementation is actively maintained, as are several commercially supported systems.
Forth typically combines a compiler with an integrated command shell, where the user interacts via subroutines called words.
Words can be defined, tested, redefined, and debugged without recompiling or restarting the whole program. All syntactic elements, including variables, operators, and control flow, are defined as words. A stack is used to pass parameters between words, leading to a Reverse Polish notation style. (Full article...) -
Image 12In computing, a compiler is software that translates computer code written in one programming language (the source language) into another language (the target language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.
There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A cross-compiler produces code for a different CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A bootstrap compiler is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimized compiler for a language.
Related software include decompilers, programs that translate from low-level languages to higher level ones; programs that translate between high-level languages, usually called source-to-source compilers or transpilers; language rewriters, usually programs that translate the form of expressions without a change of language; and compiler-compilers, compilers that produce compilers (or parts of them), often in a generic and reusable way so as to be able to produce many differing compilers. (Full article...) -
Image 13
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine code instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported.
The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, Coding for A.R.C.. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an assembler. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Computer, who, however, used the term to mean "a program that assembles another program consisting of several sections into a single program". The conversion process is referred to as assembly, as in assembling the source code. The computational step when an assembler is processing a program is called assembly time.
Because assembly depends on the machine code instructions, each assembly language is specific to a particular computer architecture such as x86 or ARM. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Large supercomputers such as IBM's Blue Gene/P are designed to heavily exploit parallelism.
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different forms of parallel computing: bit-level, instruction-level, data, and task parallelism. Parallelism has long been employed in high-performance computing, but has gained broader interest due to the physical constraints preventing frequency scaling. As power consumption (and consequently heat generation) by computers has become a concern in recent years, parallel computing has become the dominant paradigm in computer architecture, mainly in the form of multi-core processors.
In computer science, parallelism and concurrency are two different things: a parallel program uses multiple CPU cores, each core performing a task independently. On the other hand, concurrency enables a program to deal with multiple tasks even on a single CPU core; the core switches between tasks (i.e. threads) without necessarily completing each one. A program can have both, neither or a combination of parallelism and concurrency characteristics.
Parallel computers can be roughly classified according to the level at which the hardware supports parallelism, with multi-core and multi-processor computers having multiple processing elements within a single machine, while clusters, MPPs, and grids use multiple computers to work on the same task. Specialized parallel computer architectures are sometimes used alongside traditional processors, for accelerating specific tasks. (Full article...) -
Image 15

D, also known as dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is now a very different language. As it has developed, it has drawn inspiration from other high-level programming languages. Notably, it has been influenced by Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.
The D language reference describes it as follows: (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 2A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 3Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 4An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
-
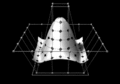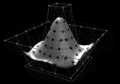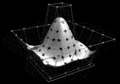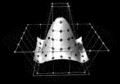
Image 5Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 6A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 7Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
-
Image 8This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 9Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
-
Image 10A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 12Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 13Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 14Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 15Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 18GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that Cornell University's student-oriented programming language dialect was made available to other universities but required a "research grant" payment in exchange?
- ... that it took a particle accelerator and machine-learning algorithms to extract the charred text of PHerc. Paris. 4 without unrolling it?
- ... that the programming language Acorn System BASIC was so non-standard that one commenter suggested that using it on the BBC Micro would be a disaster?
- ... that the study of selection algorithms has been traced to an 1883 work of Lewis Carroll on how to award second place in single-elimination tournaments?
- ... that a pink skin for Mercy in the video game Overwatch helped raise more than $12 million for breast cancer research?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
No recent news
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus