The Amu Darya, Amudarya (Template:Lang-uz, Template:Lang-fa Darya means sea, ocean or river), is the longest river in Central Asia. Amu is said to have come from the city of Āmul, now known as Türkmenabat. It is formed by the junction of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers. Local Uzbekis, Afghani and Tajiki tribes sometimes refer to the river as Ghon, or Dghon which was thought to be a derivative of Dgihun, its traditional name locally.
| Amu Darya | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Aral Sea |
| Length | 1,500 km (2,400 mi) |
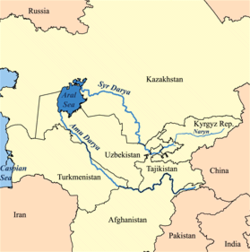
The river is navigable for over 1,450 km (800 miles). Its total length is 2,400 km (1,500 miles) and its drainage basin totals 534,739km² in area, providing a mean discharge of around 55 cubic kilometres of water per year, all of which comes from the high mountains in the south where annual precipitation can be over 1000 mm. Even before large-scale irrigation began, high summer evaporation meant that not all of this discharge reached the Aral Sea - though there is some evidence the large Pamir glaciers provided enough meltwater for the Aral to overflow during the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries A.D.
In Classical Antiquity, the river was known as the Oxus in Greek. It was traditionally known as Jayhun or Gihun in ancient Arabic sources, likely influenced by the traditional name given to it by the people who inhabited its surrounding region.
One of the claimed source of the Amu Darya is the Pamir River, which emerges from Lake Zorkul, flowing east until Ishtragh, where it turns north and then east north-west through the Hindu Kush as the Panj, forming the border of Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and subsequently the border of Afghanistan and Uzbekistan for about 200 km, passing Termez and the Afghanistan-Uzbekistan Friendship Bridge. It follows the border of Afghanistan and Turkmenistan for another 100 km before it flows into Turkmenistan at Kerki. As Amudarya, it flows across Turkmenistan south to north, passing Turkmenabat, and forms the border of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan from Khalkabad. It is then split into many waterways that used to form the river delta joining the Aral Sea, passing Urgench, Dashoguz and other cities, but it does not reach what is left of the sea anymore and is lost in the desert.
Another claimed source of the Amu Darya is an ice cave at the end of the Waghjir Valley, located in the Wakhan Corridor, in the Pamir mountains, on the border with Pakistan. The glacial river turns into the Wakhan river and joins the Pamir River about 50 Km downstream.
Use of water from the Amu Darya for irrigation has been a major contributing factor in the shrinking of the Aral Sea since the late 1950s.
Historical records state that in different periods the river flowed into the Aral Sea (from the south), the Caspian Sea (from the east) or both, similar to the Syr Darya (Jaxartes, in Ancient Greek).
References
- Curzon, George Nathaniel. 1896. The Pamirs and the Source of the Oxus. Royal Geographical Society, London. Reprint: Elibron Classics Series, Adamant Media Corporation. 2005. ISBN 1402159838 (pbk; ISBN 1402130902 (hbk).
- Gordon, T. E. 1876. The Roof of the World: Being the Narrative of a Journey over the high plateau of Tibet to the Russian Frontier and the Oxus sources on Pamir. Edinburgh. Edmonston and Douglas. Reprint by Ch’eng Wen Publishing Company. Taipei. 1971.
- Toynbee, Arnold J. 1961. Between Oxus and Jumna. London. Oxford University Press.
- Wood, John, 1872. A Journey to the Source of the River Oxus. With an essay on the Geography of the Valley of the Oxus by Colonel Henry Yule. London: John Murray.