Portal:Computer programming
Portal maintenance status: (September 2019)
|
The Computer Programming Portal
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application ___domain, details of programming languages and generic code libraries, specialized algorithms, and formal logic.
Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include analyzing requirements, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), implementation of build systems, and management of derived artifacts, such as programs' machine code. While these are sometimes considered programming, often the term software development is used for this larger overall process – with the terms programming, implementation, and coding reserved for the writing and editing of code per se. Sometimes software development is known as software engineering, especially when it employs formal methods or follows an engineering design process. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

The Greek lowercase omega (ω) character is used to represent Null in database theory.
In SQL, null or NULL is a special marker used to indicate that a data value does not exist in the database. Introduced by the creator of the relational database model, E. F. Codd, SQL null serves to fulfill the requirement that all true relational database management systems (RDBMS) support a representation of "missing information and inapplicable information". Codd also introduced the use of the lowercase Greek omega (ω) symbol to represent null in database theory. In SQL,NULLis a reserved word used to identify this marker.
A null should not be confused with a value of 0. A null indicates a lack of a value, which is not the same as a zero value. For example, consider the question "How many books does Adam own?" The answer may be "zero" (we know that he owns none) or "null" (we do not know how many he owns). In a database table, the column reporting this answer would start with no value (marked by null), and it would not be updated with the value zero until it is ascertained that Adam owns no books.
In SQL, null is a marker, not a value. This usage is quite different from most programming languages, where a null value of a reference means it is not pointing to any object. (Full article...) -
Image 2Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to perceive their environment and use learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals.
High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); generative and creative tools (e.g., language models and AI art); and superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., chess and Go). However, many AI applications are not perceived as AI: "A lot of cutting edge AI has filtered into general applications, often without being called AI because once something becomes useful enough and common enough it's not labeled AI anymore."
Various subfields of AI research are centered around particular goals and the use of particular tools. The traditional goals of AI research include learning, reasoning, knowledge representation, planning, natural language processing, perception, and support for robotics. To reach these goals, AI researchers have adapted and integrated a wide range of techniques, including search and mathematical optimization, formal logic, artificial neural networks, and methods based on statistics, operations research, and economics. AI also draws upon psychology, linguistics, philosophy, neuroscience, and other fields. Some companies, such as OpenAI, Google DeepMind and Meta, aim to create artificial general intelligence (AGI)—AI that can complete virtually any cognitive task at least as well as a human. (Full article...) -
Image 3The history of artificial intelligence (AI) began in antiquity, with myths, stories, and rumors of artificial beings endowed with intelligence or consciousness by master craftsmen. The study of logic and formal reasoning from antiquity to the present led directly to the invention of the programmable digital computer in the 1940s, a machine based on abstract mathematical reasoning. This device and the ideas behind it inspired scientists to begin discussing the possibility of building an electronic brain.
The field of AI research was founded at a workshop held on the campus of Dartmouth College in 1956. Attendees of the workshop became the leaders of AI research for decades. Many of them predicted that machines as intelligent as humans would exist within a generation. The U.S. government provided millions of dollars with the hope of making this vision come true.
Eventually, it became obvious that researchers had grossly underestimated the difficulty of this feat. In 1974, criticism from James Lighthill and pressure from the U.S.A. Congress led the U.S. and British Governments to stop funding undirected research into artificial intelligence. Seven years later, a visionary initiative by the Japanese Government and the success of expert systems reinvigorated investment in AI, and by the late 1980s, the industry had grown into a billion-dollar enterprise. However, investors' enthusiasm waned in the 1990s, and the field was criticized in the press and avoided by industry (a period known as an "AI winter"). Nevertheless, research and funding continued to grow under other names. (Full article...) -
Image 4Prolog is a logic programming language that has its origins in artificial intelligence, automated theorem proving, and computational linguistics.
Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic. Unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is intended primarily as a declarative programming language: the program is a set of facts and rules, which define relations. A computation is initiated by running a query over the program.
Prolog was one of the first logic programming languages and remains the most popular such language today, with several free and commercial implementations available. The language has been used for theorem proving, expert systems, term rewriting, type systems, and automated planning, as well as its original intended field of use, natural language processing. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Flowchart of using successive subtractions to find the greatest common divisor of number r and s
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ ⓘ) is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning).
In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results. For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation.
As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing "output" and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input. (Full article...) -
Image 6

D, also known as dlang, is a multi-paradigm system programming language created by Walter Bright at Digital Mars and released in 2001. Andrei Alexandrescu joined the design and development effort in 2007. Though it originated as a re-engineering of C++, D is now a very different language. As it has developed, it has drawn inspiration from other high-level programming languages. Notably, it has been influenced by Java, Python, Ruby, C#, and Eiffel.
The D language reference describes it as follows: (Full article...) -
Image 7
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine code instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported.
The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, Coding for A.R.C.. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an assembler. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Computer, who, however, used the term to mean "a program that assembles another program consisting of several sections into a single program". The conversion process is referred to as assembly, as in assembling the source code. The computational step when an assembler is processing a program is called assembly time.
Because assembly depends on the machine code instructions, each assembly language is specific to a particular computer architecture such as x86 or ARM. (Full article...) -
Image 8Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced /ˌɛsˌkjuˈɛl/ S-Q-L; or alternatively as /ˈsiːkwəl/ ⓘ "sequel")
is a ___domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
Introduced in the 1970s, SQL offered two main advantages over older read–write APIs such as ISAM or VSAM. Firstly, it introduced the concept of accessing many records with one single command. Secondly, it eliminates the need to specify how to reach a record, i.e., with or without an index.
Originally based upon relational algebra and tuple relational calculus, SQL consists of many types of statements, which may be informally classed as sublanguages, commonly: data query language (DQL), data definition language (DDL), data control language (DCL), and data manipulation language (DML). (Full article...) -
Image 9
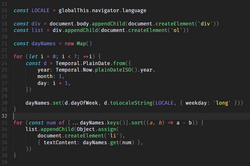
Source code for a computer program written in the JavaScript language. It demonstrates the appendChild method. The method adds a new child node to an existing parent node. It is commonly used to dynamically modify the structure of an HTML document.
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. It is one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program in its human-readable form is called source code. Source code needs another computer program to execute because computers can only execute their native machine instructions. Therefore, source code may be translated to machine instructions using a compiler written for the language. (Assembly language programs are translated using an assembler.) The resulting file is called an executable. Alternatively, source code may execute within an interpreter written for the language.
If the executable is requested for execution, then the operating system loads it into memory and starts a process. The central processing unit will soon switch to this process so it can fetch, decode, and then execute each machine instruction. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Julia is a dynamic general-purpose programming language. As a high-level language, distinctive aspects of Julia's design include a type system with parametric polymorphism, the use of multiple dispatch as a core programming paradigm, just-in-time (JIT) compilation and a parallel garbage collection implementation. Notably Julia does not support classes with encapsulated methods but instead relies on the types of all of a function's arguments to determine which method will be called.
By default, Julia is run similarly to scripting languages, using its runtime, and allows for interactions, but Julia programs/source code can also optionally be sent to users in one ready-to-install/run file, which can be made quickly, not needing anything preinstalled.
Julia programs can reuse libraries from other languages (or itself be reused from other); Julia has a special no-boilerplate keyword allowing calling e.g. C, Fortran or Rust libraries, and e.g. PythonCall.jl uses it indirectly for you, and Julia (libraries) can also be called from other languages, e.g. Python and R, and several Julia packages have been made easily available from those languages, in the form of Python and R libraries for corresponding Julia packages. Calling in either direction has been implemented for many languages, not just those and C++. (Full article...) -
Image 11
William Henry Gates III CFR (born October 28, 1955) is an American businessman and philanthropist. A pioneer of the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s and 1980s, he co-founded the software company Microsoft in 1975 with his childhood friend Paul Allen. Following the company's 1986 initial public offering (IPO), Gates became a billionaire in 1987—then the youngest ever, at age 31. Forbes magazine ranked him as the world's wealthiest person for 18 out of 24 years between 1995 and 2017, including 13 years consecutively from 1995 to 2007. He became the first centibillionaire in 1999, when his net worth briefly surpassed $100 billion. According to Forbes, as of May 2025, his net worth stood at US$115.1 billion, making him the thirteenth-richest individual in the world.
Born and raised in Seattle, Washington, Gates was privately educated at Lakeside School, where he befriended Allen and developed his computing interests. In 1973, he enrolled at Harvard University, where he took classes including Math 55 and graduate level computer science courses, but he dropped out in 1975 to co-found and lead Microsoft. He served as its CEO for the next 25 years and also became president and chairman of the board when the company incorporated in 1981. Succeeded as CEO by Steve Ballmer in 2000, he transitioned to chief software architect, a position he held until 2008. He stepped down as chairman of the board in 2014 and became technology adviser to CEO Satya Nadella and other Microsoft leaders, a position he still holds. He resigned from the board in 2020.
Over time, Gates reduced his role at Microsoft to focus on his philanthropic work with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the world's largest private charitable organization, which he and his then-wife Melinda French Gates co-chaired from 2000 until 2024. Focusing on areas including health, education, and poverty alleviation, Gates became known for his efforts to eradicate transmissible diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, and polio. After French Gates resigned as co-chair following the couple's divorce, the foundation was renamed the Gates Foundation, with Gates as its sole chair. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Margaret Elaine Hamilton (née Heafield; born August 17, 1936) is an American computer scientist. She directed the Software Engineering Division at the MIT Instrumentation Laboratory, where she led the development of the on-board flight software for NASA's Apollo Guidance Computer for the Apollo program. She later founded two software companies, Higher Order Software in 1976 and Hamilton Technologies in 1986, both in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Hamilton has published more than 130 papers, proceedings, and reports, about sixty projects, and six major programs. She coined the term "software engineering", stating "I began to use the term 'software engineering' to distinguish it from hardware and other kinds of engineering, yet treat each type of engineering as part of the overall systems engineering process."
On November 22, 2016, Hamilton received the Presidential Medal of Freedom from president Barack Obama for her work leading to the development of on-board flight software for NASA's Apollo Moon missions. (Full article...) -
Image 13The Antikythera mechanism (/ˌæntɪkɪˈθɪərə/ AN-tik-ih-THEER-ə, US also /ˌæntaɪkɪˈ-/ AN-ty-kih-) is an ancient Greek hand-powered orrery (model of the Solar System). It is the oldest known example of an analogue computer. It could be used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games similar to an olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games.
The artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. In 1902, during a visit to the National Archaeological Museum in Athens, it was noticed by Greek politician Spyridon Stais as containing a gear, prompting the first study of the fragment by his cousin, Valerios Stais, the museum director. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size 34 cm × 18 cm × 9 cm (13.4 in × 7.1 in × 3.5 in), was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is about 13 cm (5 in) in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. All these fragments of the mechanism are kept at the National Archaeological Museum, along with reconstructions and replicas, to demonstrate how it may have looked and worked.
In 2005, a team from Cardiff University led by Mike Edmunds used computer X-ray tomography and high resolution scanning to image inside fragments of the crust-encased mechanism and read the faintest inscriptions that once covered the outer casing. These scans suggest that the mechanism had 37 meshing bronze gears enabling it to follow the movements of the Moon and the Sun through the zodiac, to predict eclipses and to model the irregular orbit of the Moon, where the Moon's velocity is higher in its perigee than in its apogee. This motion was studied in the 2nd century BC by astronomer Hipparchus of Rhodes, and he may have been consulted in the machine's construction. There is speculation that a portion of the mechanism is missing and it calculated the positions of the five classical planets. The inscriptions were further deciphered in 2016, revealing numbers connected with the synodic cycles of Venus and Saturn. (Full article...) -
Image 14Mya was an intelligent personal assistant under development by Motorola. Proposed features for the program included the ability to read emails and answer questions 24 hours a day. Mya was intended to work with an internet service Motorola was developing called Myosphere, and was planned to be a paid service that would eventually be used by other mobile carriers. A female computer-generated character was created to represent Mya in advertising. While the quality of the character's animation was praised, it received criticism for being over sexualised.
Both the character and the program were announced to the public via an advertisement in March 2000, though the program was not ready for use at that time. Despite the announcement generating a considerable amount of attention, little was heard regarding the project in subsequent months. The program was never officially released nor cancelled, though the trademarks for both Myosphere and Mya were abandoned by Motorola in 2002. The name Mya was believed to be a play on the words 'My assistant'. (Full article...) -
Image 15In computing, a compiler is software that translates computer code written in one programming language (the source language) into another language (the target language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.
There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A cross-compiler produces code for a different CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A bootstrap compiler is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimized compiler for a language.
Related software include decompilers, programs that translate from low-level languages to higher level ones; programs that translate between high-level languages, usually called source-to-source compilers or transpilers; language rewriters, usually programs that translate the form of expressions without a change of language; and compiler-compilers, compilers that produce compilers (or parts of them), often in a generic and reusable way so as to be able to produce many differing compilers. (Full article...)
Selected images
-
Image 2Partial map of the Internet based on the January 15, 2005 data found on opte.org. Each line is drawn between two nodes, representing two IP addresses. The length of the lines are indicative of the delay between those two nodes. This graph represents less than 30% of the Class C networks reachable by the data collection program in early 2005.
-
Image 4An IBM Port-A-Punch punched card
-
Image 5GNOME Shell, GNOME Clocks, Evince, gThumb and GNOME Files at version 3.30, in a dark theme
-
Image 6A view of the GNU nano Text editor version 6.0
-
Image 7Partial view of the Mandelbrot set. Step 1 of a zoom sequence: Gap between the "head" and the "body" also called the "seahorse valley".
-
Image 8A head crash on a modern hard disk drive
-
Image 9Output from a (linearised) shallow water equation model of water in a bathtub. The water experiences 5 splashes which generate surface gravity waves that propagate away from the splash locations and reflect off of the bathtub walls.
-
Image 10A lone house. An image made using Blender 3D.
-
Image 13Margaret Hamilton standing next to the navigation software that she and her MIT team produced for the Apollo Project.
-
Image 14Deep Blue was a chess-playing expert system run on a unique purpose-built IBM supercomputer. It was the first computer to win a game, and the first to win a match, against a reigning world champion under regular time controls. Photo taken at the Computer History Museum.
-
Image 15Grace Hopper at the UNIVAC keyboard, c. 1960. Grace Brewster Murray: American mathematician and rear admiral in the U.S. Navy who was a pioneer in developing computer technology, helping to devise UNIVAC I. the first commercial electronic computer, and naval applications for COBOL (common-business-oriented language).
-
Image 16This image (when viewed in full size, 1000 pixels wide) contains 1 million pixels, each of a different color.
-
Image 17Ada Lovelace was an English mathematician and writer, chiefly known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. She was the first to recognize that the machine had applications beyond pure calculation, and to have published the first algorithm intended to be carried out by such a machine. As a result, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Image 18Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and in theoretical physics.
Did you know? - load more entries

- ... that both Thackeray and Longfellow bought paintings by Fanny Steers?
- ... that NATO was once targeted by a group of "gay furry hackers"?
- ... that a "hacker" with blog posts written by ChatGPT was at the center of an online scavenger hunt promoting Avenged Sevenfold's album Life Is but a Dream...?
- ... that it took a particle accelerator and machine-learning algorithms to extract the charred text of PHerc. Paris. 4 without unrolling it?
- ... that Cornell University's student-oriented programming language dialect was made available to other universities but required a "research grant" payment in exchange?
- ... that Phil Fletcher as Hacker T. Dog caused Lauren Layfield to make the "most famous snort" in the United Kingdom in 2016?
Subcategories
WikiProjects
- There are many users interested in computer programming, join them.
Computer programming news
No recent news
Topics
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus