The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism[1] is a four-bar mechanism that converts rotational motion to approximate straight-line motion with approximate constant velocity.[2] The precise design trades off straightness, lack of acceleration, and the proportion of the driving rotation that is spent in the linear portion of the full curve.[3]
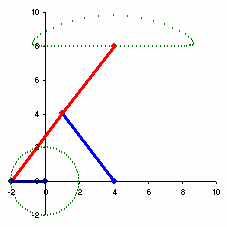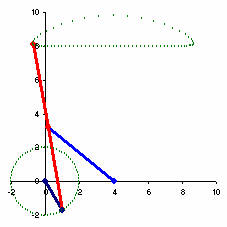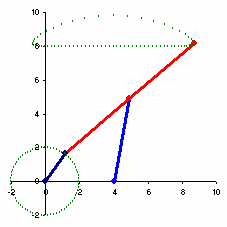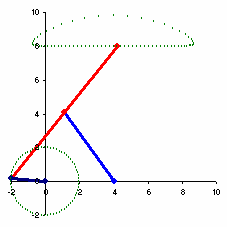


The example to the right spends over half of the cycle in the near straight portion.
The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism is a cognate linkage of the Chebyshev linkage.
The linkage was first shown in Paris on the Exposition Universelle (1878) as "The Plantigrade Machine".[4][5]
The Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism looks like the Greek letter lambda, therefore the linkage is also known as Lambda Mechanism.[6]
See also
References
- ^ http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ChebyshevsLambdaMechanism/
- ^ Design of Machinery. 2011.
- ^ DOM p134 Hoecken linkage (PDF).
- ^ http://mech.spbstu.ru/Dzenushko_Dainis:_Walking_mechanisms_survey#The_Chebyshev_Walking_Mechanism
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-11-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-11-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chebyshev's Lambda Mechanism.
- Hoeckens approximate straight-line mechanism (diagram and table of lengths)
- Hoeckens straight line linkage (Homemade example)
- Video of computer simulation of Tchebychev walking machine (Стопоход Чебышева).
- alexdenouden.nl - Rectilinear motion after "Tchebychev"
- A simulation using the Molecular Workbench software
- How does a Hoecken's Linkage Work? (Interactive Flash Animation)