The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its ___location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Hurricane Andrew was a compact, but very powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It was the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures damaged or destroyed, and remained the costliest in financial terms until Hurricane Irma surpassed it 25 years later. Andrew was also the strongest landfalling hurricane in the United States in decades and the costliest hurricane to strike anywhere in the country, until it was surpassed by Katrina in 2005.
Andrew is one of only four tropical cyclones to make landfall in the continental United States as a Category 5, alongside the 1935 Labor Day hurricane, 1969's Camille, and 2018's Michael. While the storm also caused major damage in The Bahamas and Louisiana, the greatest impact was felt in South Florida, where the storm made landfall as a Category 5 hurricane, with 1-minute sustained wind speeds as high as 165 mph (266 km/h) and a gust as high as 174 mph (280 km/h). (Full article...)
Selected article -
The 1970 Bhola cyclone (also known as the Great Cyclone of 1970 or simply the Bhola Cyclone) was the deadliest tropical cyclone on record, as well as one of the deadliest humanitarian disasters ever recorded. It struck East Pakistan (present-day Bangladesh) and India's West Bengal on 12 November 1970. At least 300,000 people died in the storm, possibly as many as 450,000, primarily as a result of the storm surge that flooded much of the low-lying islands of the Ganges Delta. Bhola was the sixth and strongest cyclonic storm of the 1970 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.
The cyclone formed over the central Bay of Bengal on 8 November and traveled northward, intensifying as it did so. It reached its peak with winds of 185 km/h (115 mph) on 10 November, and made landfall on the coast of East Pakistan on the following afternoon. The storm surge devastated many of the offshore islands, wiping out villages and destroying crops throughout the region. In the most severely affected upazila Tazumuddin, over 45% of the population of 167,000 were killed by the storm. (Full article...)
Selected image -
Selected season -
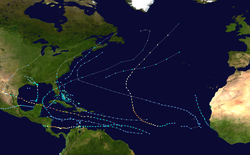
The 1988 Atlantic hurricane season was a near average season that proved costly and deadly, with 15 tropical cyclones directly affecting land. The season officially began on June 1, 1988, and lasted until November 30, 1988, although activity began on May 30 when a tropical depression developed in the Caribbean. The June through November dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first cyclone to attain tropical storm status was Alberto on August 8, nearly a month later than usual. The final storm of the year, Tropical Storm Keith, became extratropical on November 24. The season produced 19 tropical depressions of which 12 attained tropical storm status. One tropical storm was operationally classified as a tropical depression but was reclassified in post-analysis. Five tropical cyclones reached hurricane status of which three became major hurricanes reaching Category 3 on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Until the 2022 Atlantic hurricane season, it was the latest season to have multiple Atlantic-Pacific crossover storms.
There were two notable cyclones of the season, the first one being Hurricane Gilbert, which at the time was the strongest Atlantic hurricane on record. The hurricane tracked through the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico and caused devastation in Mexico and many island nations, particularly Jamaica. Its passage caused $2.98 billion in damage (1988 USD) and more than 300 deaths, mostly in Mexico. The second one was Hurricane Joan, which struck Nicaragua as a Category 4 hurricane and caused about US$1.87 billion in damage and more than 200 deaths. The hurricane crossed into the eastern Pacific Ocean and was reclassified as Tropical Storm Miriam. Hurricane Debby also successfully crossed over, becoming Tropical Depression Seventeen-E, making the 1988 season the first on record in which more than one tropical cyclone has crossed between the Atlantic and Pacific basins intact. (Full article...)
Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones
Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2025)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2025)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2025)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2025–26)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2025–26)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2025–26)
- No active systems
Last updated: 15:01, 2 September 2025 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

September 1
- 1962 - Typhoon Wanda hit Hong Kong, killing 434 people there.
- 1984 - Typhoon Ike made landfall in the southeastern Philippines with winds of 230 km/h (145 mph). Ike killed between 1,000 and 3,000 people in the Philippines and China.
- 2019 - Hurricane Dorian (pictured) reached peak intensity as a Category 5 hurricane, with peak 1-minute sustained winds of 295 km/h (185 mph), while making landfall over the Bahamas. On September 2, Dorian stalled over Grand Bahama island at Category 5 intensity for a day, causing catastrophic destruction. Dorian was known for being the strongest hurricane to make landfall and impact the islands on record.

September 2
- 1937 - A powerful typhoon struck Hong Kong, killing over 11,000 people in the British colony.
- 1985 - Hurricane Elena (pictured) made landfall as a major hurricane over southern United States, killing 9 and causing $1.3 billion in damages.

September 3
- 1935 - The 1935 Labor Day hurricane passed over the Florida Keys as a Category 5 hurricane with a central pressure of 892 hPa (mbar), making it the most intense Atlantic hurricane to make landfall in the United States measured solely by landfall intensity. It caused over $40 million of damage in Florida.
- 1988 - Hurricane Uleki (pictured) reaches peak intensity at Category 3 major hurricane intensity to the south of Hawaii where two people were also killed.
Did you know…


- …that the Australian region have three distinct lists of names for tropical storms, each one of them being administered by agencies in Autralia, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, respectively?
- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
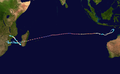
- …that Cyclone Freddy (track pictured) in 2023 was the longest-lasting tropical cyclone recorded?
- …that the typhoons of 2024—Yinxing, Toraji, Usagi, and Man-yi (pictured)—made history as the first recorded instance since 1951 of four tropical cyclones coexisting in November?
General images -

A Category 2 hurricane is a tropical cyclone which their peak intensity reaches the fourth-highest classification on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale. They are categorized with 1-minute maximum sustained winds between 83 and 95 knots (96 and 109 mph; 154 and 176 km/h; 43 and 49 m/s). Tropical cyclones that strengthen to Category 2 status and make landfall are capable of causing severe damage to human lives and infrastructure. As of 2022, a total of 89 hurricanes have peaked at Category 2 intensity within the Northeast Pacific basin, which is defined as the region of the Pacific Ocean north of the equator and east of the International Date Line. Collectively, 1,775 people have been killed as a result of Category 2 Pacific hurricanes. Storms that also attained Category 3, 4, or 5 status on the scale are not included.
There is a plethora of factors that influence tropical cyclogenesis, the formation of tropical cyclones, in the Northeastern Pacific. The North Pacific High and Aleutian Low, which occur from December to April, produce strong upper-level winds which prevents the formation of tropical cyclones. During the summer and early autumn months, sea surface temperatures are generally warm enough to support tropical cyclone development in the Northeast Pacific, and perhaps even rapid intensification. Additionally, El Niño events cause more powerful hurricanes to form by generating weaker wind shear and higher sea surface temperatures, while La Niña events reduce the number of such hurricanes by doing the opposite. (Full article...)
Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus






































